|

|
GODINA/ YEAR:
LVII.
|
ZAGREB,
30. RUJNA 2020./ 30 SEPTEMBER, 2020
|
BROJ/ NUMBER: 8.2.5.
|
CODEN POPCEA ISSN 1330-0350
INOVACIJE U PODUZEĆIMA U RAZDOBLJU 2016. – 2018.
INNOVATION ACTIVITIES IN
ENTERPRISES, 2016 – 2018
|
U razdoblju 2016. – 2018. gotovo polovica (48,2%) promatranih
poduzeća u Republici Hrvatskoj bilo je inovativno
|
|
In
the period from 2016 to 2018, almost half (48.2%) of the observed
enterprises in the Republic of Croatia were innovative
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prikazani podaci rezultat su istraživanja o inovacijskim
aktivnostima u poduzećima u razdoblju 2016. – 2018. provedenoga na uzorku
od 4 499 poduzeća. Prema tom istraživanju, inovativna poduzeća definiraju
se kao poduzeća koja su u promatranom razdoblju uvela inovaciju proizvoda
(fizičkog proizvoda ili usluge) ili inovaciju procesa.
|
|
The
presented data are the outcome of the survey on innovation activities in
enterprises in the period from 2016 to 2018 carried out on a sample of 4
499 enterprises. According to this survey, innovative enterprises are
defined as enterprises that introduced a product (good or service) or a
process innovation in the observed period.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Udio inovativnih poduzeća raste s njihovom veličinom.
Inovativno je bilo 45,8% malih poduzeća, 56,5% srednje velikih i 74,6%
velikih poduzeća. Proizvodna poduzeća prednjače u inovacijskim
aktivnostima, s udjelom od 52,4% inovativnih poduzeća, dok je 45,8% uslužnih
poduzeća bilo inovativno.
|
|
The
share of innovative enterprises grows with the enterprise size. A total of
45.8% of small enterprises were innovative, 56.5% of
medium-sized and 74.6% of large ones.
Industrial enterprises had the largest share in innovation activities (52.4%),
while 45.8% of service enterprises were innovative.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inovativna poduzeća sudjeluju u ostvarenju 69,4% ukupnog
prometa svih promatranih poduzeća u 2018. Taj trend primjećuje se i među
zaposlenima te je 64,2% svih zaposlenih u 2018. bilo zaposleno u
inovativnim poduzećima. Gledano prema veličini inovativnih poduzeća,
najveći udio u ukupnom prometu poduzeća ostvaruju velika poduzeća (87,8%),
srednje velika poduzeća ostvaruju 65,0%, dok je za mala poduzeća udio
iznosio 43,9%.
|
|
Innovative
enterprises generated 69.4% of the total turnover of all observed
enterprises in 2018. This trend is also noticeable among persons in
employment, as 64.2% of all persons in employment in 2018 were employed in
innovative enterprises. Observing by the size of innovative enterprises,
the largest share in the total turnover of enterprises was generated by
large enterprises (87.8%), medium-sized enterprises generated 65.0%, while
small enterprises generated 43.9%.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gledano prema vrsti inovacije, najčešće se provodi usporedno
uvođenje inovacije proizvoda i procesa (29,0% svih poduzeća), dok je samo
inovaciju procesa provodilo 13,0% poduzeća, a samo inovaciju proizvoda
provodilo je 5,8% svih poduzeća. Usporedno uvođenje i inovacije proizvoda i
inovacije procesa najzastupljenije je u velikim poduzećima (52,8%).
|
|
As
regards the type of innovation, the most frequent was simultaneous product
and process innovation (introduced by 29.0% of all enterprises), while
process innovation only was introduced by 13.0% of enterprises and product
innovation only by 5.8% of all enterprises. The simultaneous introduction
of product and process innovation was most frequent in large enterprises
(52.8%).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inovacijske
izdatke imalo je 26,2% poduzeća, od čega su najčešći izdaci za inovacijske
aktivnosti (izdvaja 24,0% poduzeća), dok manji broj poduzeća izdvaja za vlastite
aktivnosti IR-a (6,0%) te za vanjske usluge IR-a (4,4%).
|
|
Expenditure
on innovation was incurred by 26.2% of enterprises, of which the most
frequent was expenditure on innovation activities (incurred by 24.0% of
enterprises), while a smaller number of enterprises incurred expenditure on
R&D performed in-house (6.0%) and on external R&D (4.4%).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Poduzeća
najčešće samostalno provode inovacije proizvoda (22,4%), kao i inovacije
procesa (31,3%), dok manji broj poduzeća u suradnji s drugima provodi
inovacije proizvoda (11,7%) i inovacije procesa (13,8%).
|
|
Enterprises
most frequently developed product innovation by itself (22.4%), as well as
process innovation (31.3%), while a smaller number of enterprises developed
product innovation together with other enterprises or institutions (11.7%),
as well as process innovation (13.8%).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Previsoki
troškovi (26,1%), manjak vlastitih sredstava za inovacije (22,2%) te drukčiji
prioriteti unutar poduzeća najčešći su čimbenici koji otežavaju donošenje
odluke poduzeća o pokretanju inovacijskih aktivnosti.
|
|
The
most frequent hampering factors for innovation were too high costs (26.1%),
lack of internal finance for innovation (22.2%) and different priorities
within enterprises.
|
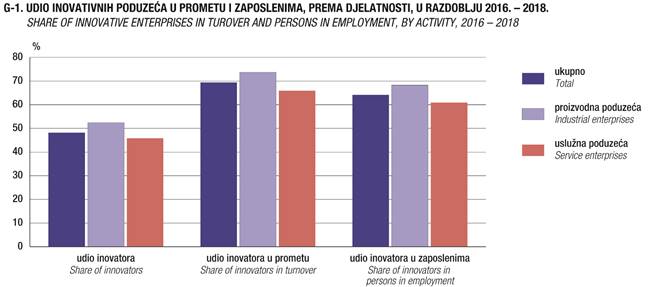
1. PODUZEĆA PREMA INOVATIVNOSTI, DJELATNOSTI I VELIČINI U
RAZDOBLJU 2016. – 2018.1)
ENTERPRISES,
BY INNOVATION PERFORMANCE, ACTIVITY AND SIZE, 2016
– 20181)
|
|
Ukupno
Total
|
Inovatori
Innovators
|
Poduzeća
koja ne inoviraju
Non-innovators
|
Udio inovatora, %
Share of innovators, %
|
Udio inovatora u prometu2), %
Share
of innovators in turnover2), %
|
Udio inovatora u zaposlenima2), %
Share
of innovators in persons in employment2), %
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ukupno
|
11 063
|
5 327
|
5 735
|
48,2
|
69,4
|
64,2
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proizvodna
poduzeća
|
3 966
|
2 077
|
1 889
|
52,4
|
73,7
|
68,3
|
Industrial
enterprises
|
|
Uslužna
poduzeća
|
7 097
|
3 250
|
3 846
|
45,8
|
65,9
|
60,9
|
Service
enterprises
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mala
poduzeća
|
9 171
|
4 198
|
4 972
|
45,8
|
43,9
|
47,7
|
Small enterprises
|
|
Srednje
velika poduzeća
|
1 556
|
879
|
677
|
56,5
|
65,0
|
58,4
|
Medium-sized
enterprises
|
|
Velika
poduzeća
|
335
|
250
|
86
|
74,6
|
87,8
|
79,7
|
Large
enterprises
|
1) Katkad
ukupno ne odgovara zbroju pojedinih stavki zbog zaokruživanja.
2) Podatak
se odnosi samo na 2018.
1) Due
to the rounding, the total sum may sometimes differ from the sum obtained by
adding up of individual items.
2) Data
refers to 2018.
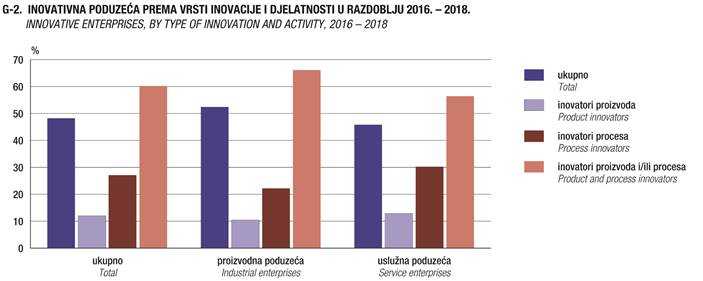
2. PODUZEĆA PREMA VRSTI INOVACIJE, DJELATNOSTI I VELIČINI U
RAZDOBLJU 2016. – 2018.
ENTERPRISES,
BY TYPE OF INNOVATION, ACTIVITY AND SIZE, 2016 – 2018
|
|
Ukupno
Total
|
Inovatori
Innovators
|
|
|
inovatori ukupno, %
Innovators total, %
|
samo inovatori proizvoda (fizičkih proizvoda i
usluga), %
Product
innovators only, %
|
samo
inovatori procesa, %
Process innovators only, %
|
inovatori
proizvoda i procesa usporedno, %
Product and process innovators simultaneously,
%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ukupno
|
11 063
|
48,2
|
5,8
|
13,0
|
29,0
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proizvodna
poduzeća
|
3 966
|
52,4
|
5,5
|
11,6
|
34,6
|
Industrial
enterprises
|
|
Uslužna
poduzeća
|
7 097
|
45,8
|
5,9
|
13,8
|
25,8
|
Service
enterprises
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mala
poduzeća
|
9 171
|
45,8
|
5,9
|
12,3
|
27,5
|
Small
enterprises
|
|
Srednje
velika poduzeća
|
1 556
|
56,5
|
5,4
|
17,1
|
32,8
|
Medium-sized
enterprises
|
|
Velika
poduzeća
|
335
|
74,6
|
5,7
|
15,2
|
52,8
|
Large
enterprises
|
3. PODUZEĆA S INOVACIJSKIM IZDACIMA PREMA VRSTI INOVACIJSKIH
IZDATAKA, DJELATNOSTI I VELIČINI U 2018.
ENTERPRISES
WITH INNOVATION EXPENDITURE, BY TYPE OF INNOVATION EXPENDITURE, ACTIVITY AND
SIZE, 2018
|
|
Ukupno
Total
|
Poduzeća s inovacijskim izdacima
Enterprises
with innovation expenditure
|
|
|
ukupno, %
Total, %
|
vrsta inovacijskih izdataka
Type
of innovation expenditure
|
|
vlastite aktivnosti IR-a, %
R&D performed in-house, %
|
vanjske usluge IR-a, %
External R&D, %
|
ostali izdaci za inovacijske aktivnosti, %
Other
innovation expenditure, %
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ukupno
|
11 063
|
26,2
|
6,0
|
4,4
|
24,0
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proizvodna
poduzeća
|
3 966
|
31,0
|
7,8
|
6,0
|
28,4
|
Industrial
enterprises
|
|
Uslužna
poduzeća
|
7 097
|
23,4
|
4,9
|
3,5
|
21,5
|
Service
enterprises
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mala
poduzeća
|
9 171
|
23,8
|
4,6
|
3,3
|
22,2
|
Small
enterprises
|
|
Srednje
velika poduzeća
|
1 556
|
34,6
|
10,2
|
8,2
|
30,5
|
Medium-sized
enterprises
|
|
Velika
poduzeća
|
335
|
51,6
|
23,0
|
17,3
|
24,0
|
Large
enterprises
|
4. INOVATIVNA
PODUZEĆA KOJA SU SAMA ILI U SURADNJI S DRUGIM PODUZEĆIMA ILI USTANOVAMA
RAZVILE INOVACIJE PROIZVODA
ILI PROCESA, PREMA DJELATNOSTI I VELIČINI PODUZEĆA, U RAZDOBLJU 2016.
– 2018.
INNOVATIVE
ENTERPRISES THAT DEVELOPED PRODUCT OR PROCESS INNOVATION BY ITSELF OR
TOGETHER WITH OTHER ENTERPRISES
OR INSTITUTIONS, BY ACTIVITY AND SIZE, 2016 – 2018
|
|
Ukupno
Total
|
Inovacije proizvoda
Product
innovation
|
Inovacije procesa
Process
innovation
|
Samostalno ili u suradnji s drugima, %
By itself or together with other enterprises
or institutions, %
|
|
|
samostalno, %
By itself, %
|
u suradnji s drugima, %
Together
with other enterprises or institutions, %
|
samostalno, %
By itself, %
|
u suradnji s drugima, %
Together with other enterprises or
institutions, %
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ukupno
|
11 063
|
22,4
|
11,7
|
31,3
|
13,8
|
42,7
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proizvodna
poduzeća
|
3 966
|
28,4
|
12,9
|
34,7
|
14,8
|
47,2
|
Industrial
enterprises
|
|
Uslužna
poduzeća
|
7 097
|
19,1
|
11,0
|
29,4
|
13,2
|
40,2
|
Service
enterprises
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mala
poduzeća
|
9 171
|
21,6
|
9,8
|
30,2
|
11,5
|
40,7
|
Small
enterprises
|
|
Srednje
velika poduzeća
|
1 556
|
24,6
|
17,4
|
34,2
|
20,6
|
49,5
|
Medium-sized
enterprises
|
|
Velika
poduzeća
|
335
|
34,3
|
36,4
|
46,9
|
44,8
|
67,8
|
Large
enterprises
|
5. ČIMBENICI
KOJI SU OTEŽALI DONOŠENJE ODLUKE PODUZEĆA O POKRETANJU INOVACIJSKIH
AKTIVNOSTI ILI NJIHOVU PROVEDBU,
PREMA VAŽNOSTI, U RAZDOBLJU 2016. – 2018.
HAMPERING
FACTORS FOR INNOVATION, BY THE DEGREE OF IMPORTANCE, 2016 ‒ 2018
|
Čimbenik ''velika važnost''
|
% svih
poduzeća
As % of all
enterprises
|
Hampering factors of “high importance”
|
|
|
|
|
|
Previsoki troškovi
|
26,1
|
Costs too
high
|
|
Manjak vlastitih sredstava za inovacije
|
22,2
|
Lack of
internal finance for innovation
|
|
Drukčiji prioriteti unutar poduzeća
|
18,2
|
Different priorities
within enterprise
|
|
Manjak kvalificiranih zaposlenika unutar poduzeća
|
17,4
|
Lack of
skilled employees within enterprise
|
|
Teškoće u dobivanju državne potpore ili subvencija
|
16,3
|
Difficulties
in obtaining public grants or subsidies
|
|
Jaka konkurencija na tržištu
|
14,8
|
Too much
competition in the market
|
|
Manjak sredstava u obliku kredita ili privatnoga
kapitala
|
14,7
|
Lack of
credit or private equity
|
|
Neizvjesna potražnja na tržištu za inovativnim
idejama
|
10,2
|
Uncertain
market demand for ideas for innovations
|
|
Manjak partnera za suradnju
|
8,7
|
Lack of
collaboration partners
|
|
Manjak pristupa vanjskom znanju
|
6,6
|
Lack of
access to external knowledge
|
|
METODOLOŠKA
OBJAŠNJENJA
|
|
NOTES
ON METHODOLOGY
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Izvor
podataka
|
|
Data
sources
|
|
|
|
|
|
Podaci
su rezultat obrade istraživanja o inovacijskim aktivnostima poduzeća u
razdoblju 2016. – 2018., koje je provedeno na uzorku od
4 499 poduzeća – pravnih i fizičkih osoba. Istraživanje je provedeno u
Državnom zavodu za statistiku i potpuno je usklađeno s istraživanjem koje
se u Europskoj uniji provodi svake dvije godine pod naslovom Community
Innovation Survey.
|
|
Data
are the outcome of the survey on innovation activities of enterprises in
the period from 2016 to 2018 carried out on the sample of 4 499 enterprises
– legal entities and natural persons. The survey was conducted by the
Croatian Bureau of Statistics and was completely harmonised with the
Community Innovation Survey, which is conducted in the European Union every
two years
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Obuhvat
i usporedivost
|
|
Coverage
and comparability
|
|
|
|
|
|
Osnovni
skup za statističko istraživanje o inovacijskim aktivnostima poduzeća u
razdoblju 2016. – 2018. izdvojen je iz Statističkoga poslovnog registra
Državnog zavoda za statistiku (stanje na kraju 2018.) i sadržava
11 313 jedinica (9 989 poduzeća – pravnih i fizičkih osoba – i
1 324 obrtnika) s 10 ili više zaposlenih i s glavnom djelatnošću
navedenom među sljedećim djelatnostima:
|
|
The
basic group for the statistical survey on innovation activities of
enterprises in the period from 2016 to 2018 was extracted from the
Statistical Business Register of the Croatian Bureau of Statistics
(situation as at the end of 2018) and contained 11 313 enterprises
(9 989 enterprises – legal entities and natural persons and 1 324
crafts) employing 10 or more persons and with a prevailing activity
classified among the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Odjeljak
|
Naziv
|
|
Division
|
Description
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
05 –
09
|
Rudarstvo i vađenje
|
|
05
– 09
|
Mining and
quarrying
|
|
10 –
33
|
Prerađivačka industrija
|
|
10
– 33
|
Manufacturing
|
|
35
|
Opskrba električnom energijom, plinom,
parom i klimatizacija
|
|
35
|
Electricity, gas,
steam and air conditioning supply
|
|
36 –
39
|
Opskrba vodom; uklanjanje otpadnih voda,
gospodarenje
|
|
36
– 39
|
Water supply;
sewerage, waste management and
|
|
|
otpadom te djelatnosti sanacije okoliša
|
|
|
remediation activities
|
|
46
|
Trgovina na veliko, osim vozila i
motocikla
|
|
46
|
Wholesale trade,
except of motor vehicles and motorcycles
|
|
49 –
53
|
Prijevoz i skladištenje
|
|
49
– 53
|
Transportation and
storage
|
|
58 –
63
|
Informacije i komunikacije
|
|
58
– 63
|
Information and
communication
|
|
64 –
66
|
Financijske djelatnosti i djelatnosti
osiguranja
|
|
64
– 66
|
Financial and
insurance activities
|
|
71
|
Arhitektonske djelatnosti i inženjerstvo;
tehničko ispitivanje
i analiza
|
|
71
|
Architectural and
engineering activities; technical testing
and analysis
|
|
72
|
Znanstveno
istraživanje i razvoj
|
|
72
|
Scientific
research and development
|
|
73
|
Promidžba
i istraživanje tržišta
|
|
73
|
Advertising and
marketing research
|
|
41 –
43
|
Građevinarstvo
|
|
41
– 43
|
Construction
|
|
55 –
56
|
Djelatnosti pružanja smještaja te
pripreme i usluživanja hrane
|
|
55
– 56
|
Accommodation and
food service activities
|
|
68
|
Poslovanje nekretninama.
|
|
68
|
Real estate activities
|
|
|
|
|
|
Osnovni
skup stratificiran je po djelatnostima, veličini razreda s obzirom na broj
zaposlenih i regijama.
|
|
The
basic group was stratified according to the activities, size classes
according to the number of persons in employment and regions.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Veličine razreda jesu:
|
|
Size classes were
as follows:
|
|
10
– 49
|
zaposlenih – mala poduzeća
|
|
10
– 40
|
persons in
employment – small enterprises
|
|
50
– 249
|
zaposlenih – srednje velika poduzeća
|
|
50
– 249
|
persons in
employment – medium-sized enterprises
|
|
250 +
|
zaposlenih – velika poduzeća.
|
|
250
+
|
persons in
employment – large enterprises
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Uzorak
za istraživanje o inovacijskim aktivnostima poduzeća u razdoblju 2016. –
2018. uključuje sva srednje velika i velika poduzeća u osnovnom skupu i
stratificirani slučajni uzorak malih poduzeća. Alokacija uzorka po
stratumima proporcionalna je broju jedinica u stratumu. Proporcionalna
alokacija narušena je time što je u stratumima poduzeća s djelatnošću u
građevinarstvu, trgovini na veliko, djelatnošću pružanja smještaja te
pripreme i usluživanja hrane i djelatnošću proizvodnje kruha smanjen broj
jedinica u uzorku s obzirom na broj koji je bio izračunan da bi se smanjila
inače velika zastupljenost tih djelatnosti u uzorku i povećao broj jedinica
u uzorku u drugim stratumima.
|
|
The
sample for the survey on innovation activities of enterprises in the period
from 2016 to 2018 included all medium-sized and large enterprises in the
basic group and a stratified random sample of small enterprises. The sample
allocation to strata was proportional to the number of units in the
stratum. The proportional allocation was disrupted due to the cutting of
the number of units in the sample in the strata of enterprises engaged in
the activities Construction, Wholesale trade, Accommodation and food
service activities and Manufacture of bread in relation to the number that
had been calculated in order to reduce otherwise large representation of
the said activities in the sample and to increase the number of sample
units in other strata.
|
|
|
|
|
|
U
stratumima u kojima je uzorak veći od populacije, veličina uzorka jednaka
je veličini populacije; u stratumima u kojima je izračunana veličina uzorka
manja od 6, ako je i veličina populacije manja od 6, uzorak je jednak
populaciji, a ako je veličina populacije veća ili jednaka 6, veličina
uzorka jest 6.
|
|
In
the strata where the sample was bigger than the population, the sample size
equalled the population size; in the strata where the calculated sample
size was smaller than 6 and the population size less than 6, the sample
equalled population, while if the population size was 6 or more, the sample
size was 6.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Konačna
veličina uzorka iznosila je 4 499 poduzeća – pravnih i fizičkih osoba.
|
|
The
final sample size was 4 499 enterprises – legal entities and natural
persons.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stopa
odgovora poduzeća koja su ispunila upitnik iznosila je 73,5%.
|
|
The
response rate of enterprises that filled in the questionnaire was 73.5%.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Zbog
promjena u metodologiji (u definicijama inovacija) podaci se ne mogu
izravno uspoređivati s prethodnim razdobljima.
|
|
Due
to changes in the methodology (in definitions of innovations), the data
cannot be directly compared with previous periods.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Statistička
klasifikacija djelatnosti upotrijebljena u ovom istraživanju jest Nacionalna
klasifikacija djelatnosti – NKD 2007.
|
|
The
statistical classification of activities used in this survey was the
National Classification of Activities – NKD 2007.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sljedeća
tablica prikazuje procjene, standardne pogreške procjena, intervale pouzdanosti
(95%) i koeficijente varijacije za udio inovativnih poduzeća prema veličini
i djelatnosti.
|
|
The
following table shows estimates, standard
estimation errors, confidence intervals (95%) and variation coefficients
for the share of innovative enterprises by size and activity.
|
|
|
Udio inovativnih poduzeća
Share of innovative enterprises
|
|
|
procjena
Estimate
|
standardna pogreška
Standard estimation error
|
interval pouzdanosti
Confidence interval
|
koeficijent varijacije
Variation coefficient
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ukupno
|
48,2%
|
1,1%
|
46,0%
: 50,4%
|
2,3%
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prema veličini
|
|
|
|
|
By size
|
|
Mala
|
45,8%
|
1,3%
|
43,1%
: 48,4%
|
2,9%
|
Small
|
|
Srednje velika
|
56,5%
|
0,7%
|
55,1%
: 57,9%
|
1,3%
|
Medium-sized
|
|
Velika
|
74,4%
|
1,1%
|
72,3%
: 76,5%
|
1,4%
|
Large
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prema djelatnosti
|
|
|
|
|
By activity
|
|
Proizvodna
|
52,4%
|
1,4%
|
49,6%
: 55,1%
|
2,7%
|
Industrial
|
|
Uslužna
|
45,8%
|
1,6%
|
42,8%
: 48,9%
|
3,4%
|
Service
|
Definicije
i objašnjenja
|
|
Definitions
and explanations
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inovativna
poduzeća jesu
ona poduzeća koja su u svom poslovanju u razdoblju 2016. – 2018. uvela novi
ili poboljšani proizvod ili poslovni proces (ili njihovu kombinaciju) koji
se znatno razlikuje od prethodnih proizvoda ili poslovnih procesa u
poduzeću i uveden je na tržište (proizvod) ili se počeo primjenjivati u
poduzeću (proces). Inovacija proizvoda mora biti dostupna potencijalnim
korisnicima, ali ne mora nužno utjecati na prodaju. Inovacija poslovnog
procesa uvedena je kad se poduzeće počne kontinuirano njome koristiti u
svojim operacijama (poslovnim aktivnostima).
|
|
Innovative
enterprises are all business entities that introduced
a new or improved product or process (or their combination) in the period
from 2016 to 2018, which significantly differs from previous products or
business processes in the enterprise and was introduced to the market
(product) or started to be applied in the enterprise (process). Product
innovation must be available to potential customers, but it does not
necessarily affect sales. Business process innovation is introduced when an
enterprise starts using it continuously in its operations (business
activities).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inovacija
proizvoda jest
novi ili poboljšani fizički proizvod ili usluga uveden na tržište koji se
znatno razlikuje od prethodnih proizvoda ili od usluga poduzeća. Proizvodi
uključuju opipljive predmete i digitalne proizvode te softver. Usluge su
neopipljive aktivnosti koje se proizvode i konzumiraju istodobno, npr.
maloprodaja, bankarske usluge, hotelski smještaj, osiguranje, obrazovni
tečajevi, zračni prijevoz, savjetodavne usluge itd. Inovacija
proizvoda uključuje znatne promjene u dizajnu fizičkog proizvoda ili
usluge i digitalne proizvode ili usluge. Ona isključuje čistu
preprodaju novih proizvoda i usluga te promjene estetske prirode.
|
|
Product
innovation is a new or improved good or service
introduced to the market, which differs significantly from the enterprise’s
previous goods or services. Products include tangible objects and digital
products, as well as software. Services are intangible activities that are
produced and consumed at the same time, e.g. retail, banking services,
hotel accommodation, insurance, educational courses, air transport,
consulting services, etc. Product innovation includes significant
changes in the design of a good or service and digital products or
services. It excludes pure resale of new products and services and
aesthetic changes.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inovacija
poslovnog procesa
jest novi ili poboljšani poslovni proces uveden u poduzeću za jednu ili
više poslovnih funkcija koji se znatno razlikuje od prethodnih poslovnih
procesa poduzeća.
|
|
Business
process innovation is a new or improved business process
introduced in an enterprise for one or more business functions, which
differs significantly from the enterprise’s previous business processes.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inovacijska
aktivnost obuhvaća
sve razvojne, financijske i komercijalne aktivnosti koje poduzeće poduzima
s namjerom razvijanja ili uvođenja inovacije.
|
|
Innovation
activity includes all development, financial and
commercial activities that an enterprise undertakes with the intention of
developing or introducing an innovation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inovatori proizvoda jesu
poduzeća koja su u razdoblju 2016. – 2018. uvela inovaciju proizvoda i/ili
usluge.
|
|
Product
innovators are enterprises that introduced a product
and/or service innovation in the period from 2016 to 2018.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inovatori procesa
jesu poduzeća koja su u razdoblju 2016. – 2018. uvela inovaciju poslovnog
procesa
|
|
Process
innovators are business entities that introduced a
business process innovation in the period from 2016 to 2018.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proizvodne
djelatnosti u
ovom istraživanju jesu: Rudarstvo i vađenje (05 – 09), Prerađivačka
industrija (10 – 33), Opskrba električnom energijom, plinom, parom i
klimatizacija (35) i Opskrba vodom; uklanjanje otpadnih voda, gospodarenje
otpadom te djelatnosti sanacije okoliša (36 – 39).
|
|
Industrial
activities in this survey are as follows: Mining
and quarrying (05 – 09), Manufacturing (10 – 33), Electricity, gas, steam
and air conditioning supply (35) and Water supply; sewerage, waste
management and remediation activities (36 – 39).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Uslužne
djelatnosti
u ovom istraživanju jesu: Građevinarstvo (41 – 43), Trgovina na veliko,
osim vozila i motocikla (46)*, Prijevoz i skladištenje (49 – 53),
Djelatnosti pružanja smještaja te pripreme i usluživanja hrane (55 – 56),
Informacije i komunikacije (58 – 63), Financijske djelatnosti i djelatnosti
osiguranja (64 – 66), Poslovanje nekretninama (68), Arhitektonske
djelatnosti i inženjerstvo; tehničko ispitivanje i analiza (71)*,
Znanstveno istraživanje i razvoj (72)*, Promidžba i istraživanje tržišta
(73)*.
|
|
Service
activities in this survey are as follows:
Construction (41 – 43), Wholesale trade, except of motor vehicles and
motorcycles (46)*, Transportation and storage (49 – 53), Accommodation and
food service activities (55 – 56), Information and communication (58 – 63),
Financial and insurance activities (64 – 66), Real estate activities (68),
Architectural and engineering activities; technical testing and analysis
(71)*, Scientific research and development (72)*, Advertising and marketing
research (73)*.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Djelatnosti
označene zvjezdicom uključene su u analizu inovacijskih aktivnosti zbog
važnosti koju imaju u gospodarstvu Republike Hrvatske.
|
|
Activities
marked with an asterisk are included in the analysis of innovation
activities because of their significance in the Croatian economy.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mala
poduzeća
jesu poduzeća s 10 do 49 zaposlenih.
|
|
Small
enterprises are enterprises employing 10 to 49
persons.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Srednja
poduzeća jesu
poduzeća s 50 do 249 zaposlenih.
|
|
Medium-sized
enterprises are enterprises employing 50 to 249
persons.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Velika
poduzeća
jesu poduzeća s 250 i više zaposlenih.
|
|
Large
enterprises are enterprises employing 250 and more
persons.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Istraživanje
i razvoj (IR) jest
kreativni sustavni stvaralački rad s ciljem uvećavanja količine znanja
uključujući znanja o čovječanstvu, kulturi i društvu te razvoj novih
primjena dostupnog znanja.
|
|
Research
and development (R&D) comprise creative
and systematic work undertaken in order to increase the stock of knowledge
– including knowledge of humankind, culture and society – and to
devise new applications of available knowledge.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vlastite
aktivnosti istraživanja i razvoja podrazumijevaju aktivnosti istraživanja
i razvoja (IR-a) koje je poduzeće obavilo za stvaranje novog znanja ili
rješavanje znanstvenih ili tehničkih problema (uključuje razvoj softvera
unutar poduzeća). Također uključuje tekuće izdatke, troškove rada i
kapitalne izdatke na zgrade i opremu posebno za istraživanje i razvoj (IR).
|
|
In-house
R&D includes the R&D activities
undertaken by an enterprise to create new knowledge or solve scientific or
technical issues (including software development within the enterprise). It
also includes current expenditures, labour costs and capital expenditure on
buildings and equipment specifically for R&D.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vanjske
usluge istraživanja i razvoja obuhvaćaju iste aktivnosti kao što je
spomenuto u gornjoj definiciji, koje je poduzeće ugovorilo s drugim
poduzećima (uključujući druga poduzeća unutar svoje grupe poduzeća) ili s javnim
ili privatnim istraživačkim ustanovama.
|
|
External
R&D includes the same activities as in the
above definition, which are contracted-out to other enterprises (including
other enterprises within its own enterprise group) or to public or private
research institutions.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ostali
izdaci za inovacijske aktivnosti uključuju nabavu postrojenja, softvera,
prava intelektualnog vlasništva ili zgrada za inovacijske aktivnosti, osim
IR-a;
nabavu
znanja od drugih poduzeća ili ustanova za inovacijske aktivnosti, osim IR-a
(npr. patenti, licencije, žigovi); dizajn proizvoda ili usluge te priprema
proizvodnje/distribucije za inovacijske aktivnosti, osim IR-a;
osposobljavanje i profesionalni razvoj zaposlenika za inovacijske
aktivnosti, osim IR-a (npr. obuka zaposlenika ili kontinuirana izobrazba); marketing
inovacija (marketinške aktivnosti izravno povezane s inovacijama,
uključujući istraživanje tržišta).
|
|
Other
innovation expenditure includes the acquisition
of machinery equipment, software, intellectual property rights or buildings
for innovation activities other than R&D; the acquisition of external
knowledge for innovation activities other than R&D (e.g. patents,
licenses, trademarks); product or service design, and the preparation of
production/distribution for innovation activities other than R&D;
employee training and professional development for innovation activities
other than R&D (e.g. employee training or continued education);
marketing of innovations (marketing activities directly related to innovations,
including market research).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U ovom Priopćenju objavljuju se podaci istraživanja koje je
provedeno uz financijsku pomoć Europske unije. Za njegov sadržaj odgovoran
je isključivo Državni zavod za statistiku te ni u kojem slučaju ne izražava
stav Europske unije.
|
|
The survey whose data are published in this First Release has
been conducted with the financial assistance of the European Union. The
contents of this document are the sole responsibility of the Croatian
Bureau of Statistics and can under no circumstances be regarded as
reflecting the position of the European Union.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kratice
|
|
Abbreviations
|
|
|
|
|
|
NKD 2007.
|
Nacionalna klasifikacija djelatnosti,
verzija 2007.
|
|
NKD 2007.
|
National
Classification of Activities, 2007 version
|
|
IR
|
istraživanje i razvoj
|
|
R&D
|
research and
development
|
Objavljuje Državni zavod za statistiku Republike
Hrvatske, Zagreb, Ilica 3, p. p. 80.
Published by the Croatian Bureau of Statistics, Zagreb,
Ilica 3, P. O. B. 80
Telefon/ Phone: +385 (0) 1
4806-111, telefaks/ Fax: +385 (0) 1 4817-666
Novinarski upiti/ Press corner:
press@dzs.hr
Odgovorne osobe:
Persons responsible:
Milenka Primorac Čačić, načelnica Sektora poslovnih
statistika
Milenka Primorac Čačić, Director of Business Statistics
Directorate
Lidija Brković, glavna ravnateljica
Lidija Brković, Director
General
Priredili: Matija Škegro Vdović i Željko
Jelovečki
Prepared by: Matija Škegro Vdović and
Željko Jelovečki
|
|
MOLIMO
KORISNIKE DA PRI KORIŠTENJU PODATAKA NAVEDU IZVOR.
USERS ARE KINDLY
REQUESTED TO STATE THE SOURCE.
|
|
Služba za odnose s korisnicima i zaštitu
podataka
Customer Relations and Data Protection
Department
|
Informacije i
korisnički zahtjevi
Information and user requests
|
|
Pretplata
publikacija
Subscription
|
|
|
|
|
Telefon/ Phone: +385 (0)
1 4806-138, 4806-154
Elektronička pošta/ E-mail:
stat.info@dzs.hr
Telefaks/ Fax: +385 (0) 1 4806-148
|
|
Telefon/ Phone: +385
(0) 1 4806-115
Elektronička pošta/ E-mail:
prodaja@dzs.hr
Telefaks/ Fax: +385 (0) 1 4806-148
|
|



