Contents
![]() Quality Declaration of the
Quality Declaration of the
European Statistical System
Quality
|
|
Efficient and timely preparation and dissemination
of quality statistical indicators, which reflect economic and social
phenomena and processes, and provide users with a reliable source for
analysis of the current situation and decision making, are among the main
tasks of the Croatian statistical system. The Croatian Bureau of Statistics, in all working phases - from the
collection, processing, production to the dissemination of statistics,
takes care about the quality of statistical processes, the final results or
products and the level of services provided to its users. That the quality is becoming an increasingly important factor is
confirmed by the European Statistical System Vision 2020, which, by
implementing a holistic approach to statistics, aims at achieving a higher
quality of statistical products and services. The use of new data sources
makes the quality a comprehensive element in the statistical production
process and a driver of new forms of cooperation that encourage users of
statistical products and services to involve in the statistical processes,
which consequently contributes to the smooth businesses progress. Following the example of the European Statistical
System, the Croatian Bureau of Statistics has developed a model of the Total
Quality Management based on the Code of Practice of European Statistics. It
is the model that is fully adjusted to the statistical purposes, because
working on the quality of statistical processes, final products and services
is not the same as the standard quality monitoring of products and services
of profit-oriented business entities on the market. In statistical terms, the
quality is focused on obtaining statistical products and services with the
characteristics that will enable and simplify successful planning and
conducting of economic policy. Therefore all statistical activities are
focused on achieving this goal by tracking the following six basic quality
features:
|
|
|
|
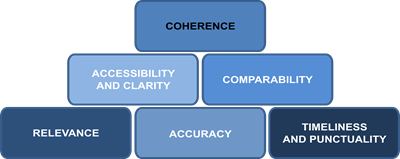
Coherence |
Refers to the data compliance with similar data from
other sources. The problems with data compliance may appear when data come
from completely different sources or statistical surveys, in which process
the applied concepts, classifications and methodological standards are not
harmonised, i.e. coherent. |
||
|
Accessibility |
Imply simple and user-oriented access to the
statistical data. The Accessibility of statistical results or products and
services relates to specific physical circumstances in which the data are
available to the user: location at which the data are accessible by users,
terms of use, downloading types and methods for use, publication date,
availability of microdata and macrodata,
possibility of use in different formats and media (i.
e. paper, computer files, CD-ROM, internet). The clarity refers to the statistical information environment in which
users obtain the information: whether textual information is associated with
the data, methodological notes, documentation; whether the data are equipped
with charts and other graphical presentations; whether the information on the
quality of data is available; whether additional information for users is
available, if necessary (all the above specified is contained in the term
"metadata"). |
||
|
Comparability: |
Relates to the need that the obtained data and
information are comparable in time, between geographical areas and between
different domains. |
||
|
Relevance: |
Is the degree to
which statistics meet current and future users' needs.
In other words, whether the statistics produced reflect real and objective
users' needs, whether their expectations are met by conducted surveys and
whether appropriate measures are applied (definitions, classifications,
etc.). |
||
|
Accuracy: |
Indicates a potential difference between estimated
and actual data on population. Statistical
data do not equal the actual values due to variability and bias. |
||
|
Timeliness and punctuality: |
Timeliness of data publication refers to the length
of time between periods when a statistical phenomenon was observed and the
date of data publishing, while the punctuality refers to the period between
the scheduled publishing date (for example, in the Calendar of Statistical
Data Issues) and the actual date of the data publishing. |
||